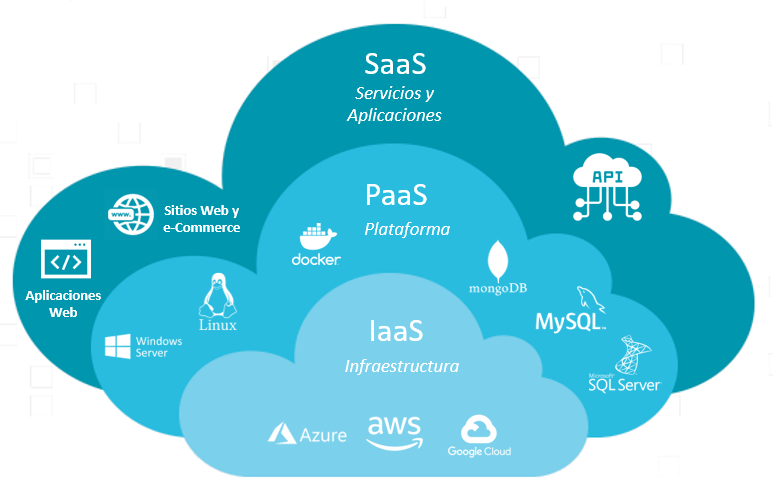
The Cloud Computing Trilogy: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
In the age of the digital transformation, cloud computing has become a fundamental pillar in the world of technology. It offers an array of services that empower businesses, organizations, and individuals to leverage the power of computing without the need for costly infrastructure. Three core cloud service models underpin this technology: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Let’s dive into the details of each one to understand how they shape our digital landscape.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS lays the foundation for cloud computing by providing the basic building blocks for IT infrastructure. In an IaaS model, a third-party cloud provider delivers virtualized computing resources over the internet. These resources often include virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities. IaaS allows organizations to forgo the hassle of procuring and maintaining physical servers, storage, and networking hardware. Instead, they can flexibly scale their computing power up or down as needed, paying only for the resources they consume.
The flexibility and cost-efficiency of IaaS make it an attractive choice for businesses. It empowers them to launch and manage virtual servers, storage, and network resources while retaining control over the operating systems, applications, and data that run on these virtualized environments. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Moving up the cloud computing hierarchy, we find Platform as a Service (PaaS). PaaS adds an extra layer of abstraction by offering not only the infrastructure but also a development and deployment platform. In this model, developers can create, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure and operating systems. PaaS is particularly valuable for software developers, as it streamlines the application development and deployment process.
PaaS providers offer a comprehensive platform that includes tools, development frameworks, databases, and application hosting. This approach accelerates the development cycle and reduces time-to-market for applications. PaaS providers, such as Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service, allow developers to focus on coding and innovation while the platform manages scaling, security, and maintenance.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
At the apex of the cloud service model hierarchy is Software as a Service (SaaS). SaaS is the most user-friendly of the three models, as it delivers ready-made software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. This eliminates the need for users to download or install software on their local devices. Instead, they can access the software through a web browser, enjoying the benefits of remote access and automatic updates.
SaaS spans a wide range of applications, from email and office productivity tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, to customer relationship management (CRM) software like Salesforce, and many more. Businesses, institutions, and individuals can leverage SaaS solutions for improved efficiency, collaboration, and cost savings.
In conclusion, the cloud computing trilogy of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offers a spectrum of options for organizations and individuals. IaaS provides the foundational infrastructure, PaaS streamlines development and deployment, and SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications. Each model caters to distinct needs, allowing users to choose the level of control, customization, and management that suits them best in the dynamic world of cloud computing. As technology continues to advance, these cloud service models will remain key players in shaping the digital landscape for years to come.
Leave a Reply